The world faces three major challenges: climate change, food security, and the need for renewable energy. An innovative solution now addresses all three simultaneously. Agrivoltaics combines solar energy production with agriculture on the same land. This groundbreaking approach transforms farming communities worldwide through sustainable land use.
What is Agrivoltaics?
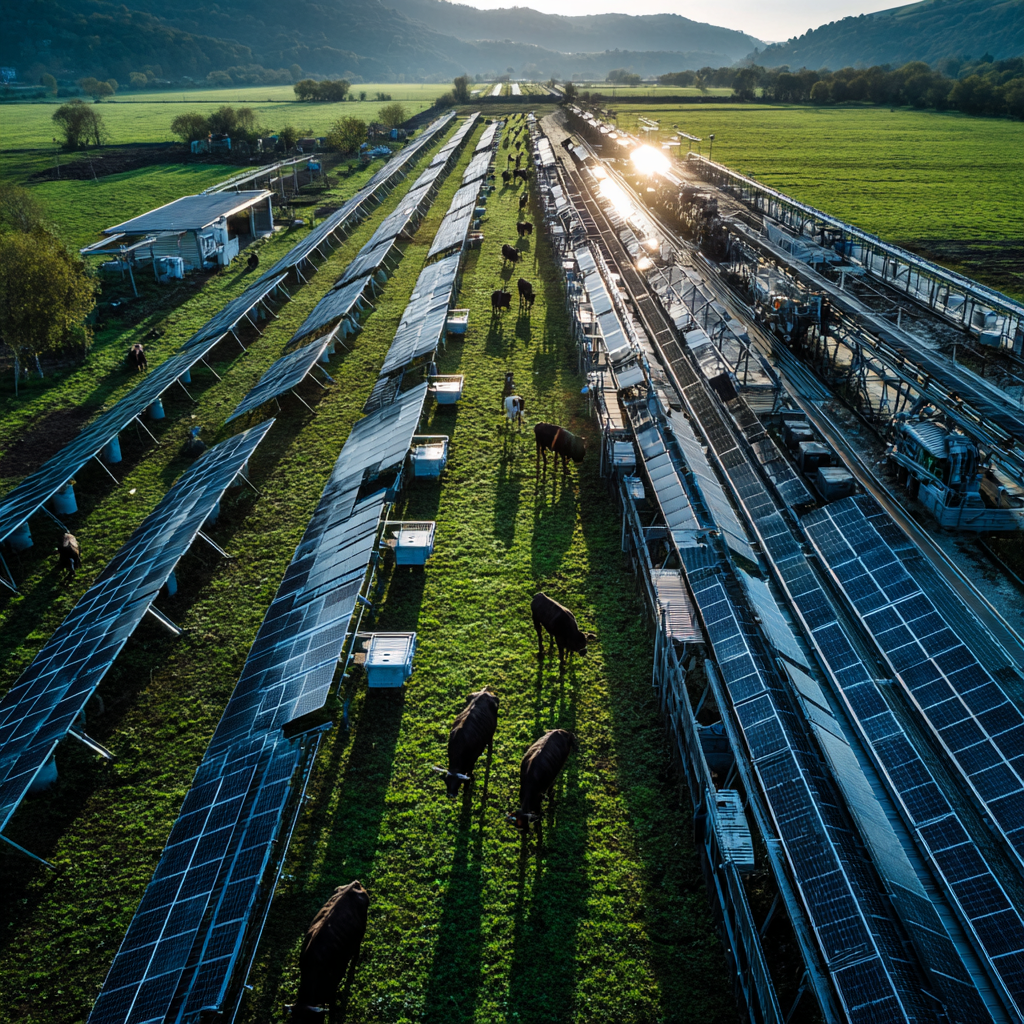
Agrivoltaics integrates land management systems in a unique way. Farmers generate solar electricity while continuing agricultural production on the same plot. This innovative approach strategically places solar panels above or between crops. The result creates a symbiotic relationship between renewable energy generation and food production.
German researcher Adolf Goetzberger first developed this concept in the 1980s. Recent technological advances have made agrivoltaics increasingly viable. Growing concerns about land scarcity now attract farmers, energy developers, and policymakers to this solution.
How Does Agrivoltaics Work?
Thoughtful design and engineering make agrivoltaics successful. Workers typically mount solar panels on elevated structures 8-15 feet above the ground. This height allows farming equipment to operate underneath. The panels can remain fixed or include tracking systems that follow the sun’s movement throughout the day.
Key design considerations include:
Engineers space solar arrays to optimize both energy production and crop growth. This design allows sufficient sunlight to reach plants below. At the same time, it maximizes electricity generation.
Crop Selection: Certain crops thrive under partial shade conditions created by solar panels. Leafy greens, herbs, berries, and some vegetables often perform well in agrivoltaic systems.
Water Management: The panels can collect rainwater for irrigation, improving water efficiency – a crucial benefit in drought-prone regions.
Access and Maintenance: Systems are designed with adequate clearance for farming equipment, ensuring agricultural operations can continue seamlessly.
Benefits of Agrivoltaics
The dual-use approach of agrivoltaics creates multiple benefits for farmers, communities, and the environment.
Economic Advantages
Farmers participating in agrivoltaic projects typically earn additional income through land lease agreements with solar developers. Alternatively, they can own and operate the solar installation themselves. This diversified revenue stream provides financial stability during challenging agricultural seasons or market fluctuations.
Research shows that agrivoltaic systems can generate 30% more economic value than standalone solar installations. They maintain agricultural productivity on the same land.
Agricultural Benefits
Many agrivoltaic installations demonstrate improved agricultural outcomes rather than reduced crop yields. The partial shade from solar panels can:
- Reduce heat stress on crops during extreme weather
- Decrease water evaporation, improving irrigation efficiency
- Protect plants from hail and severe weather conditions
- Create more favorable growing conditions for shade-tolerant crops
Researchers have shown that some crops produce higher yields under agrivoltaic systems compared to traditional open-field farming. These crops include lettuce, spinach, and tomatoes.
Environmental Impact
This approach maximizes land use efficiency rather than converting agricultural land to solar farms. The same acreage serves dual purposes. This preserves farmland while advancing renewable energy goals.
Additional environmental benefits include reduced soil erosion, improved biodiversity through varied microclimates, and decreased pesticide use due to the protective environment created by solar panels.
Real-World Applications and Success Stories
Agrivoltaic projects are gaining momentum across the globe, with successful implementations demonstrating the concept’s viability across different climates and agricultural systems.
In Massachusetts, the state’s Solar Massachusetts Renewable Target (SMART) program provides financial incentives for agrivoltaic projects, leading to numerous successful installations combining solar energy with cranberry farming, sheep grazing, and vegetable production.
France has emerged as a leader in agrivoltaics research and implementation, with projects spanning from wine production to livestock grazing. The country’s supportive policies and research initiatives have created a thriving agrivoltaic sector.
Japan has been pioneering agrivoltaics since the early 2000s, with over 2,000 installations combining rice farming with solar energy production. The Japanese model has demonstrated that agrivoltaics can work effectively even in densely populated areas with limited land availability.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its promise, agrivoltaics faces several challenges that must be addressed for widespread adoption.
Higher Initial Costs: Agrivoltaic installations typically cost 10-15% more than ground-mounted solar systems due to the elevated mounting structures and specialized engineering required.
Technical Complexity: Designing systems that optimize both agricultural and energy production requires specialized expertise and careful planning.
Regulatory Hurdles: Many regions lack specific regulations or incentive programs for agrivoltaic projects, creating uncertainty for developers and farmers.
Crop Limitations: Not all crops are suitable for agrivoltaic systems, limiting the agricultural applications in certain regions.
The Technology Behind Agrivoltaics
Modern agrivoltaic systems incorporate advanced technologies to maximize both agricultural and energy outcomes. Tracking systems allow panels to follow the sun while optimizing light conditions for crops below. Smart sensors monitor soil moisture, temperature, and light levels to inform both irrigation and panel positioning decisions.
Bifacial solar panels, which can generate electricity from both sides, are particularly well-suited for agrivoltaic applications. These panels can capture reflected light from the ground surface while allowing more light to reach crops compared to traditional panels.
Future Outlook for Agrivoltaics
The agrivoltaics market is projected to grow significantly over the next decade, driven by increasing demand for renewable energy, concerns about food security, and supportive government policies. The U.S. Department of Energy has identified agrivoltaics as a key strategy for achieving solar energy goals while preserving agricultural land.
Technological innovations continue to improve system efficiency and reduce costs. Researchers are developing specialized solar panels designed specifically for agricultural applications, advanced monitoring systems, and automated farming equipment compatible with agrivoltaic installations.
Getting Started with Agrivoltaics
Farmers interested in agrivoltaics should begin by assessing their land’s suitability, considering factors such as solar resource availability, crop compatibility, and local regulations. Consulting with agrivoltaic specialists, solar developers, and agricultural extension services can provide valuable guidance for project development.
Financial considerations include evaluating potential solar lease income against current agricultural revenue, understanding available incentives, and assessing long-term economic benefits. Many states offer specific programs supporting agrivoltaic development, making projects more financially viable.
Conclusion
Agrivoltaics represents a paradigm shift in how we approach land use, energy production, and agriculture. By combining solar energy generation with farming activities, this innovative approach offers a sustainable solution to multiple global challenges while providing economic benefits to rural communities.
As technology continues to advance and supportive policies emerge, agrivoltaics is poised to play an increasingly important role in our transition to a sustainable energy future. For farmers, communities, and policymakers seeking solutions that address climate change while supporting agricultural livelihoods, agrivoltaics offers a compelling path forward.
The future of farming may well be under the protective canopy of solar panels, where crops and clean energy grow together in harmony.
For more detailed information on this topic: National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) Agrivoltaics Page