When you think of buying land in Texas or selling land in Texas, zoning laws might not be the first thing that comes to mind—but they should be. These regulations play a crucial role in determining what you can and cannot do with a piece of property. From residential plots to commercial spaces, understanding zoning laws can save you headaches down the road. Let’s unpack the essentials of zoning laws in a way that’s easy to grasp.
What Are Zoning Laws?
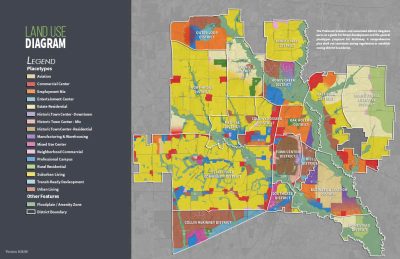
Zoning laws are rules set by local governments to regulate how land within a specific area can be used. These laws divide land into categories like residential, commercial, industrial, and agricultural zones. Think of zoning as a neighborhood blueprint—it dictates whether your dream home can be built on a plot or if a commercial building can pop up next to it.
Why Do Zoning Laws Matter?
For anyone buying land in Texas, zoning laws define what your land can be used for. Want to start a farm? Ensure the land is zoned for agriculture. Dreaming of opening a boutique? You’ll need a commercial designation. On the flip side, for those selling land in Texas, understanding zoning laws can make your property more appealing to potential buyers by highlighting its permissible uses.
Zoning Categories Explained
- Residential Zones
These zones are for housing, whether single-family homes, duplexes, or apartment complexes. If you’re buying land to build your dream home, check if it’s in a residential zone. - Commercial Zones
Commercial zones allow businesses to thrive. From retail shops to office spaces, these areas are strictly for business activities. - Agricultural Zones
Perfect for farming, ranching, or other agricultural pursuits. Texas, with its sprawling landscapes, has plenty of these zones. - Industrial Zones
If you’re planning to set up a factory or manufacturing plant, you’ll need land in an industrial zone. - Mixed-Use Zones
These areas blend residential, commercial, and sometimes industrial uses. They’re becoming popular in urban parts of Texas.
What to Check Before Buying Land in Texas
Before signing on the dotted line, here are some zoning considerations:
- Research Local Zoning Maps: Most cities and counties in Texas have online zoning maps that show the designation of each parcel of land.
- Permits and Restrictions: Some zones have strict building height limits, parking requirements, or noise regulations.
- Rezoning Possibilities: If the current zoning doesn’t align with your plans, you can request rezoning, but it’s a lengthy and uncertain process.

How Zoning Impacts Selling Land in Texas
When selling, emphasize the land’s zoning advantages. Is it perfect for residential development? Or is it in a prime commercial area? Buyers often weigh the land’s zoning designation heavily in their decision-making process.
Common Zoning Challenges
- Non-Conforming Use
If a property is being used in a way that doesn’t align with its zoning, it may face restrictions or require permits. - Zoning Changes
Local governments can rezone areas, which might impact property values or potential uses. - Environmental Regulations
Some zones come with additional rules to protect the environment, especially in areas with natural landmarks or water sources.
Tips for Navigating Zoning Laws
- Consult a Local Expert: Real estate attorneys or land-use planners in Texas can offer valuable guidance.
- Engage with Local Authorities: Speak with zoning departments to clarify any doubts before proceeding.
- Think Long-Term: Ensure the land’s zoning aligns with future plans to avoid complications.
Understanding zoning laws can feel overwhelming, but they’re there to maintain order and protect property values. Whether you’re buying land in Texas or selling land in Texas, taking the time to grasp these rules is a smart move. With a bit of research and professional advice, you’ll be well-equipped to make the most of your land investment.
Check our latest blog on How To Buy Land
G
S